Introduction
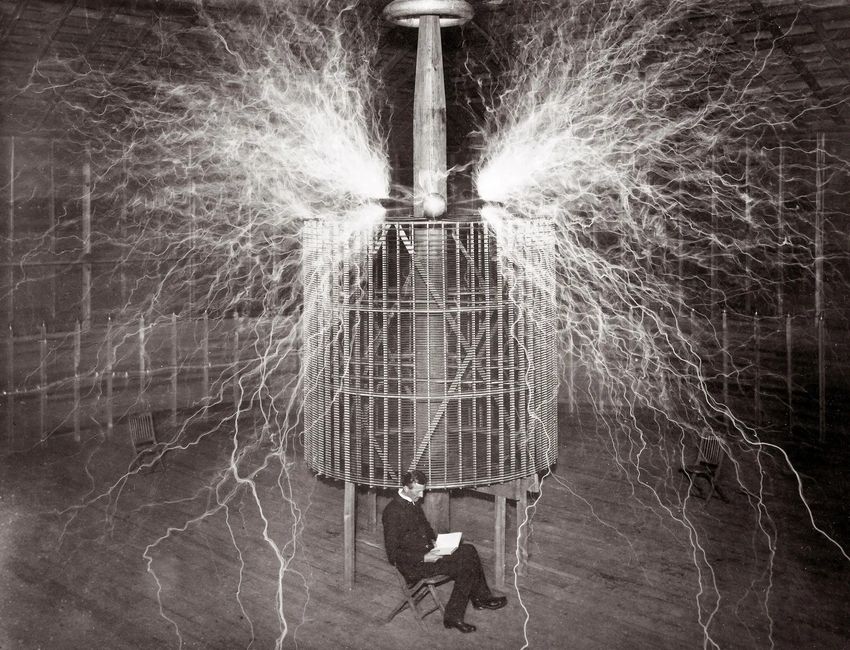
Imagine charging your smartphone without plugging it in or powering devices through thin air. Sounds like magic, right? Well, this “magic” is made possible by wireless power transfer (WPT)—a revolutionary concept pioneered by the legendary inventor Nikola Tesla. His visionary experiments laid the foundation for modern wireless charging technologies that power devices like electric toothbrushes, smartphones, and even electric vehicles. In this article, we’ll explore how wireless power transfer works, Tesla’s groundbreaking contributions, and how this technology is shaping the future of energy. ⚡🔧📡
🧠 Understanding Wireless Power Transfer (WPT)
Wireless power transfer is the process of transmitting electrical energy from a power source to a device without using physical wires. This is achieved by creating electromagnetic fields that can transfer energy through air or other mediums.
Types of Wireless Power Transfer:
- 📡 Magnetic Induction: Uses coils to create a magnetic field that transfers energy over short distances (e.g., wireless phone chargers).
- 🌐 Magnetic Resonant Coupling: Transfers energy over longer distances by tuning two coils to the same resonant frequency.
- 🛰️ Radio Waves (RF): Transmits energy over longer distances using electromagnetic waves (used in RFID tags and wireless sensors).
🌍 Nikola Tesla: The Father of Wireless Power
Nikola Tesla, one of the greatest inventors of all time, envisioned a world where electricity could be transmitted wirelessly across vast distances. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Tesla’s experiments with alternating current (AC) and electromagnetic fields laid the groundwork for wireless power transfer.
Key Contributions:
- 🏛️ Tesla Coil: Invented in 1891, this high-voltage transformer could wirelessly transmit electricity through the air, lighting lamps and powering devices without wires.
- 🗼 Wardenclyffe Tower: Tesla’s ambitious project on Long Island, New York, aimed to transmit wireless electricity across the globe. Although never completed, it demonstrated Tesla’s vision of global wireless energy.
- 📡 Resonant Coupling: Tesla discovered that energy transfer is most efficient when the transmitter and receiver are tuned to the same frequency, a principle still used in modern wireless charging systems.
⚙️ How Wireless Power Transfer Works
1. Magnetic Induction (Short Range)
The most common method of wireless power transfer is magnetic induction, used in wireless phone chargers and electric toothbrushes. Here’s how it works:
- A transmitter coil (in the charging pad) generates an alternating magnetic field.
- A receiver coil (inside the device) captures this magnetic field and converts it back into electrical energy to charge the battery.
2. Magnetic Resonant Coupling (Medium Range)
For longer distances, magnetic resonant coupling is used. Both the transmitter and receiver coils are tuned to resonate at the same frequency, allowing energy to transfer more efficiently over greater distances. This method is used in wireless electric vehicle charging and medical implants.
3. Radio Frequency (RF) Transmission (Long Range)
For long-range applications, energy can be transmitted using radio waves (RF). An RF transmitter sends electromagnetic waves through the air, which are captured by a receiver antenna and converted into electrical energy. This method is used in wireless sensors, RFID tags, and space-based solar power systems.
📱⚡ Real-World Applications of Wireless Power Transfer
🔋 1. Consumer Electronics:
- Wireless charging pads for smartphones, smartwatches, and earbuds
- Electric toothbrushes and hearing aids with inductive charging
🚗 2. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Wireless charging pads embedded in roads and parking spaces
- Reduces the need for charging cables, improving convenience and safety
🏡 3. Smart Homes and IoT Devices:
- Wireless power for smart sensors, cameras, and home automation systems
- Eliminates the need for batteries and reduces maintenance
🏥 4. Medical Devices:
- Wireless power for implanted medical devices like pacemakers and insulin pumps
- Enhances patient comfort and reduces the need for surgery to replace batteries
🌎 5. Space and Renewable Energy:
- Space-based solar power systems that transmit energy to Earth using microwave beams
- Wireless energy transfer between satellites and spacecraft
⚖️ Advantages and Challenges of Wireless Power Transfer
✅ Advantages:
- No need for cables, reducing clutter and wear-and-tear
- Increased convenience and flexibility for charging devices
- Enables charging of multiple devices simultaneously
- Safer and more reliable, with no exposed wires or connectors
⚠️ Challenges:
- Limited range, especially for magnetic induction systems
- Energy loss during transmission, reducing efficiency
- Higher costs compared to traditional wired systems
- Potential interference with other electronic devices
💡 The Future of Wireless Power Transfer
Wireless power transfer is rapidly evolving, with exciting advancements on the horizon:
- 🚗 Electric Vehicles: Wireless charging highways that power vehicles as they drive, eliminating the need for frequent charging stops.
- 🏡 Smart Homes: Entire rooms equipped with wireless power systems, allowing devices to operate without batteries or cords.
- 🌍 Global Energy Transmission: Large-scale wireless energy grids that transmit renewable energy across continents.
- 🚀 Space Applications: Space-based solar power stations that beam energy to Earth, providing clean and unlimited power.
📝 Conclusion
Nikola Tesla’s vision of wireless power transfer is no longer science fiction—it’s becoming a reality that is transforming the way we power our world. From charging smartphones to enabling electric vehicles and space-based energy systems, wireless power is revolutionizing technology and sustainability. As researchers continue to overcome challenges and improve efficiency, the future promises a world where power flows invisibly through the air, just as Tesla dreamed. So, the next time you place your phone on a wireless charger, remember that you’re witnessing the magic of Tesla’s genius! ⚡💡🚀