We now have hyperpure poly-Si, already doped to the desired level, and the next step must be to convert it to a single crystal. There are essentially two methods for crystal growth used in this case:
| Czochralski or crucible grown crystals (CZ crystals). |
| or FZ crystals. |
| The latter method produces crystals with the highest purity, but is not easily used at large diameters. 150 mm crystals are already quite difficult to make and nobody so far has made a 300 mm crystal this way. Float zone crystal growth, while the main method at the beginning of the Si age, is now only used for some specialities and therefore will not be discussed here; some details can be found in the link. |
| The Czochralski method, invented by the Polish scientist J. Czochralski in 1916, is the method of choice for high volume production of Si single crystals of exceptional quality and shall be discussed briefly. Below is a schematic drawing of a crystal growth apparatus employing the Czochralski method. More details can be found in the link. |
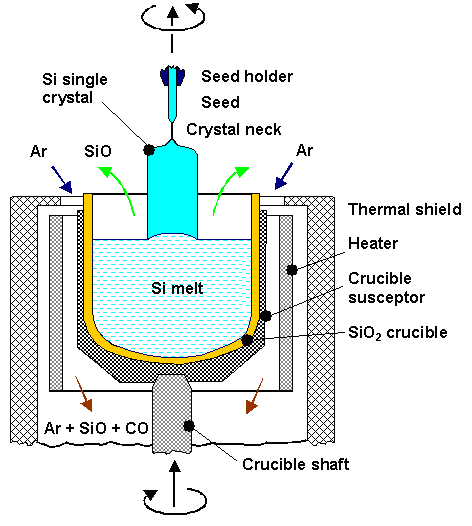 |
Essentially, a crystal is “pulled” out of a vessel containing liquid Si by dipping a seed crystal into the liquid which is subsequently slowly withdrawn at a surface temperature of the melt just above the melting point.


