Introduction
Imagine electricity as water flowing through a pipe. The amount of water flowing, the pressure pushing it, and the size of the pipe all determine how much water gets through. Similarly, in an electric circuit, Ohm’s Law helps us understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance—three essential elements that make our gadgets, lights, and appliances work. Don’t worry if this sounds technical—we’re going to break it down in the most fun and easy-to-understand way possible! 😊⚡
🧠 What Is Ohm’s Law?
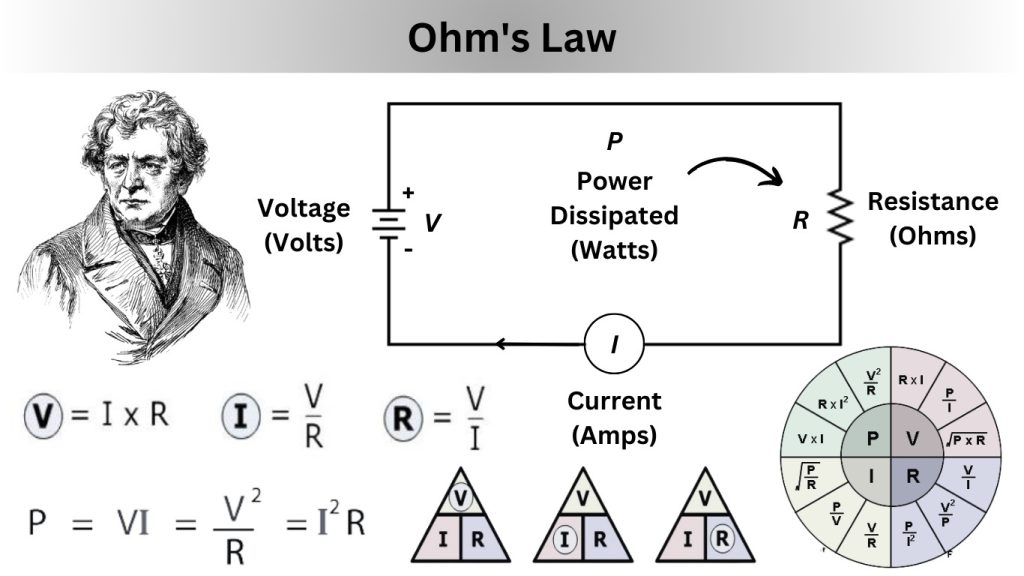
Ohm’s Law, named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Here’s the magical formula:
V = I × R
- V = Voltage (measured in volts, V) ⚡
- I = Current (measured in amperes, A) 💧
- R = Resistance (measured in ohms, Ω) 🛑
🌊💧 The Water Pipe Analogy (Making It Fun!)
- Voltage (V): The pressure that pushes water through the pipe. More pressure = faster flow! 🚿
- Current (I): The amount of water flowing through the pipe. More water = stronger flow! 🌊
- Resistance (R): The size of the pipe. A narrow pipe resists water flow, while a wider pipe lets more water pass through! 🛑
Example:
Imagine you have a garden hose connected to a faucet. Turning the faucet more increases the pressure (voltage), causing more water (current) to flow. If the hose is thin (high resistance), less water flows out. But if the hose is wide (low resistance), more water flows out!
🧩 Ohm’s Law Triangle: The Secret to Solving Any Problem!
- To find Voltage (V): V = I × R
- To find Current (I): I = V / R
- To find Resistance (R): R = V / I
💡 Real-Life Examples of Ohm’s Law
🔋 1. Lighting Up an LED:
You have a 9V battery and an LED that needs 20mA (0.02A) of current. What resistor do you need to protect the LED?
R = (9V – 2V) / 0.02A = 350 Ω
A 330Ω resistor (a standard value) is used to limit the current and prevent the LED from burning out.
💡 2. Charging Your Smartphone:
A phone charger provides 5V and the phone battery draws 1A. What’s the internal resistance of the phone’s circuit?
R = 5V / 1A = 5 Ω
🔥 3. Using an Electric Heater:
An electric heater uses 10A of current and has a resistance of 24Ω. What voltage is needed?
V = 10A × 24Ω = 240V
🎮 Fun Ohm’s Law Challenge: Test Yourself!
Question: You have a light bulb with a resistance of 120Ω connected to a 12V battery. How much current flows through the bulb?
(Scroll down for the answer! ⬇️)
Answer: I = 12V / 120Ω = 0.1A
So, 0.1A of current flows through the light bulb! 💡😊
🧩 Why Is Ohm’s Law So Important?
- ✅ Design Circuits: Ensure components receive the correct voltage and current
- 💡 Prevent Damage: Choose the right resistors to protect LEDs and other sensitive components
- ⚡ Optimize Power Use: Calculate power consumption to save energy and reduce costs
- 🧠 Troubleshoot Problems: Identify faulty components by measuring voltage, current, and resistance
💾 How Ohm’s Law Powers Your World
- 🔋 Batteries: Ensure devices receive the correct current
- 💡 Light Bulbs: Control brightness and prevent overheating
- 📱 Smartphones: Regulate power to sensitive circuits
- 🚗 Electric Cars: Optimize energy use and battery life
- 🏡 Home Appliances: Ensure safe and efficient operation
🛑 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- ⚠️ Mixing Units: Always use volts (V), amperes (A), and ohms (Ω). Convert milliamps (mA) to amps by dividing by 1,000.
- ⚠️ Ignoring Resistance: Never connect an LED directly to a battery without a resistor—it’ll burn out instantly!
- ⚠️ Reversing Voltage and Current: Remember that voltage pushes the current, while resistance limits it.
⚡💡 Ohm’s Law in Action: DIY LED Circuit
What You Need:
- 9V Battery
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
- 330Ω Resistor
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Connect the resistor to the LED in series.
- Attach the LED’s positive leg (anode) to the battery’s positive terminal.
- Connect the resistor to the battery’s negative terminal.
- Watch the LED light up! 💡✨
Why It Works:
The resistor limits the current flowing through the LED to protect it from damage. By using Ohm’s Law, we calculated the correct resistor value to ensure the LED operates safely.
🔮 The Future of Electronics and Ohm’s Law
As technology advances, understanding Ohm’s Law remains essential for designing efficient and sustainable electronics. From ultra-fast computers and electric vehicles to renewable energy systems and space exploration, Ohm’s Law plays a crucial role in powering the future.
📝 Conclusion
Congratulations! 🎉 You’ve unlocked the secret of Ohm’s Law—the key to understanding how electricity flows through circuits. By mastering the simple formula V = I × R, you can design circuits, troubleshoot electronics, and even build your own DIY projects. Remember, electricity is like water: voltage pushes it, resistance slows it down, and current is the flow that powers everything around you. So, the next time you see a glowing LED or hear the hum of an electric motor, you’ll know that Ohm’s Law is working its magic behind the scenes! ⚡💡😊