Introduction
Electricity powers our world, from lighting our homes to running massive industrial machinery. But have you ever wondered how electricity travels from power plants to your devices? The battle between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) has shaped the way we transmit and use electricity. In this article, we’ll explore the differences, advantages, and real-world applications of AC and DC, helping you understand which current reigns supreme! ⚡💡
💡 What is AC (Alternating Current)?
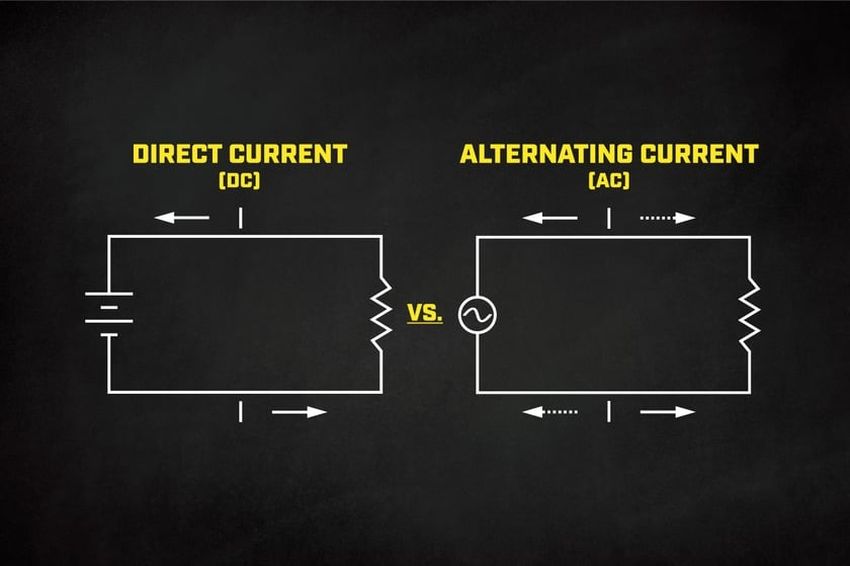
Alternating Current (AC) is a type of electrical current where the flow of electrons changes direction periodically. This back-and-forth motion typically occurs 50 to 60 times per second, depending on the region (50 Hz in Europe and Asia, 60 Hz in North America). AC is the standard form of electricity supplied to homes and businesses because it can easily travel long distances with minimal energy loss.
Key Characteristics of AC:
- 🌀 Alternates direction periodically
- 🔌 Used for household and industrial power supply
- 📏 Voltage can be easily transformed using transformers
⚡ What is DC (Direct Current)?
Direct Current (DC) flows continuously in one direction, making it ideal for electronic devices and batteries. Unlike AC, DC does not change direction, which provides a stable and consistent voltage—essential for sensitive electronics like computers, smartphones, and LED lighting.
Key Characteristics of DC:
- ➡️ Flows in one constant direction
- 🔋 Found in batteries, solar panels, and electronics
- 📏 Voltage is harder to change without complex converters
🥊 The Historical Showdown: Tesla vs. Edison
The battle between AC and DC dates back to the late 19th century, famously known as the “War of the Currents.” Thomas Edison championed DC, believing it was safer and more practical. However, Nikola Tesla, supported by George Westinghouse, promoted AC due to its ability to travel long distances with less energy loss. Ultimately, AC won the war, becoming the standard for power transmission worldwide. But DC never vanished—it found its niche in electronics and modern renewable energy systems.
⚙️ AC vs. DC: Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | AC (Alternating Current) | DC (Direct Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of Flow | Alternates back and forth 🌀 | Flows in one direction ➡️ |
| Energy Loss Over Distance | Low energy loss, ideal for long distances 🌍 | Higher energy loss over long distances ⚠️ |
| Voltage Transformation | Easily transformed using transformers ⚡ | Requires complex converters 🔄 |
| Application | Power grids, household electricity 🏡 | Electronics, batteries, solar panels ☀️🔋 |
| Safety | Higher risk of electric shock ⚡⚠️ | Safer at low voltages ✅ |
| Efficiency for Transmission | More efficient for long distances 🚚 | Less efficient over long distances 🚫 |
🌎 Modern Applications of AC and DC
🔌 AC in Everyday Life:
- Powers homes, offices, and factories
- Runs large appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines
- Used in electrical grids to transport electricity over vast distances
🔋 DC in Everyday Life:
- Powers smartphones, laptops, and LED lights
- Essential for solar panels and electric vehicles (EVs) 🚗⚡
- Provides stable power for sensitive electronics and medical devices
🌱 Renewable Energy and the Rise of DC
With the growing emphasis on renewable energy, DC is experiencing a resurgence. Solar panels and wind turbines generate DC electricity, which is then converted to AC for transmission. Additionally, electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems rely on DC, making it a key player in the shift toward a sustainable future.
💡 Which Current is Better?
The debate over AC and DC isn’t about one being better than the other—it’s about using the right current for the right job. AC is ideal for transmitting electricity over long distances, while DC is perfect for powering electronics and renewable energy systems. In fact, modern power systems increasingly use both AC and DC together, leveraging their unique strengths.
🔮 The Future of Power Transmission
As technology advances, we’re seeing new developments like High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission lines, which combine the long-distance efficiency of AC with the stable, low-loss properties of DC. These systems are becoming essential for connecting renewable energy sources to the grid, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable energy future.
📝 Conclusion
The showdown between AC and DC has shaped the world of electricity, but today, both currents play vital roles in our daily lives. AC powers our homes and cities, while DC drives our gadgets, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. As we move toward a greener and more connected world, the synergy of AC and DC will continue to electrify our future. ⚡🔋🌎